Human EPCAM knockout A-431 cell line (ab261902)
Overview
-
Product name
Human EPCAM knockout A-431 cell line
See all EpCAM lysates -
Parental Cell Line
A431 -
Organism
Human -
Mutation description
Knockout achieved by CRISPR/Cas9; X = 2 bp deletion; Frameshift: 99.58% -
Passage number
<20 -
Knockout validation
Immunocytochemistry (ICC), Next Generation Sequencing (NGS), Western Blot (WB) -
Tested applications
Suitable for: Flow Cyt, WB, Next Generation Sequencing, ICC/IFmore details -
Biosafety level
1 -
General notes
Recommended control: Human wild-type A-431 cell line (ab263975). Please note a wild-type cell line is not automatically included with a knockout cell line order, if required please add recommended wild-type cell line at no additional cost using the code WILDTYPE-TMTK1.
Cryopreservation cell medium: Cell Freezing Medium-DMSO Serum free media, contains 8.7% DMSO in MEM supplemented with methyl cellulose.
Culture medium: DMEM (High Glucose) + 10% FBS
Initial handling guidelines: Upon arrival, the vial should be stored in liquid nitrogen vapor phase and not at -80°C. Storage at -80°C may result in loss of viability.
1. Thaw the vial in 37°C water bath for approximately 1-2 minutes.
2. Transfer the cell suspension (0.8 mL) to a 15 mL/50 mL conical sterile polypropylene centrifuge tube containing 8.4 mL pre-warmed culture medium, wash vial with an additional 0.8 mL culture medium (total volume 10 mL) to collect remaining cells, and centrifuge at 201 x g (rcf) for 5 minutes at room temperature. 10 mL represents minimum recommended dilution. 20 mL represents maximum recommended dilution.
3. Resuspend the cell pellet in 5 mL pre-warmed culture medium and count using a haemocytometer or alternative cell counting method. Based on cell count, seed cells in an appropriate cell culture flask at a density of 2x104 cells/cm2. Seeding density is given as a guide only and should be scaled to align with individual lab schedules.
4. Incubate the culture at 37°C incubator with 5% CO2. Cultures should be monitored daily.Subculture guidelines:
- All seeding densities should be based on cell counts gained by established methods.
- A guide seeding density of 2x104 cells/cm2 is recommended.
- A partial media change 24 hours prior to subculture may be helpful to encourage growth, if required.
- Cells should be passaged when they have achieved 80-90% confluence.
This product is subject to limited use licenses from The Broad Institute and ERS Genomics Limited, and is developed with patented technology. For full details of the limited use licenses and relevant patents please refer to our limited use license and patent pages.
We will provide viable cells that proliferate on revival.
Properties
-
Number of cells
1 x 106 cells/vial, 1 mL -
Adherent /Suspension
Adherent -
Tissue
Skin -
Cell type
epithelial -
Disease
Epidermoid Carcinoma -
Gender
Female -
Mycoplasma free
Yes -
Storage instructions
Shipped on Dry Ice. Store in liquid nitrogen. -
Storage buffer
Constituents: 8.7% Dimethylsulfoxide, 2% Cellulose, methyl ether -
Research areas
Target
-
Function
May act as a physical homophilic interaction molecule between intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) and intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs) at the mucosal epithelium for providing immunological barrier as a first line of defense against mucosal infection. Plays a role in embryonic stem cells proliferation and differentiation. Up-regulates the expression of FABP5, MYC and cyclins A and E. -
Tissue specificity
Highly and selectively expressed by undifferentiated rather than differentiated embryonic stem cells (ESC). Levels rapidly diminish as soon as ESC's differentiate (at protein levels). Expressed in almost all epithelial cell membranes but not on mesodermal or neural cell membranes. Found on the surface of adenocarcinoma. -
Involvement in disease
Defects in EPCAM are the cause of diarrhea type 5 (DIAR5) [MIM:613217]. It is an intractable diarrhea of infancy characterized by villous atrophy and absence of inflammation, with intestinal epithelial cell dysplasia manifesting as focal epithelial tufts in the duodenum and jejunum.
Defects in EPCAM are a cause of hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer type 8 (HNPCC8) [MIM:613244]. HNPCC is a disease associated with marked increase in cancer susceptibility. It is characterized by a familial predisposition to early-onset colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and extra-colonic tumors of the gastrointestinal, urological and female reproductive tracts. HNPCC is reported to be the most common form of inherited colorectal cancer in the Western world. Clinically, HNPCC is often divided into two subgroups. Type I is characterized by hereditary predisposition to colorectal cancer, a young age of onset, and carcinoma observed in the proximal colon. Type II is characterized by increased risk for cancers in certain tissues such as the uterus, ovary, breast, stomach, small intestine, skin, and larynx in addition to the colon. Diagnosis of classical HNPCC is based on the Amsterdam criteria: 3 or more relatives affected by colorectal cancer, one a first degree relative of the other two; 2 or more generation affected; 1 or more colorectal cancers presenting before 50 years of age; exclusion of hereditary polyposis syndromes. The term 'suspected HNPCC' or 'incomplete HNPCC' can be used to describe families who do not or only partially fulfill the Amsterdam criteria, but in whom a genetic basis for colon cancer is strongly suspected. Note=HNPCC8 results from heterozygous deletion of 3-prime exons of EPCAM and intergenic regions directly upstream of MSH2, resulting in transcriptional read-through and epigenetic silencing of MSH2 in tissues expressing EPCAM. -
Sequence similarities
Belongs to the EPCAM family.
Contains 1 thyroglobulin type-1 domain. -
Post-translational
modificationsHyperglycosylated in carcinoma tissue as compared with autologous normal epithelia. Glycosylation at Asn-198 is crucial for protein stability. -
Cellular localization
Lateral cell membrane. Cell junction > tight junction. Co-localizes with CLDN7 at the lateral cell membrane and tight junction. - Information by UniProt
Associated products
-
KO cell lysates
-
Related Products
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [E144] - BSA and Azide free (ab183178)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [VU-1D9] (ab187372)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [VU-1D9] - BSA and Azide free (ab212579)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [EPR20532-222] (ab213500)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [EPR20532-225] (ab223582)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [4A7] - C-terminal (ab224826)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [EPR20532-225] - BSA and Azide free (ab225894)
- Anti-Cytokeratin 19 antibody [EPR1579Y] - BSA and Azide free (ab232566)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [E144] (ab32392)
- Anti-EpCAM antibody [323/A3] (ab85987)
Applications
The Abpromise guarantee
Our Abpromise guarantee covers the use of ab261902 in the following tested applications.
The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user.
| Application | Abreviews | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Cyt |
Use at an assay dependent concentration.
|
|
| WB |
Use at an assay dependent concentration.
|
|
| Next Generation Sequencing |
Use at an assay dependent concentration.
|
|
| ICC/IF |
Use at an assay dependent concentration.
|
| Notes |
|---|
|
Flow Cyt
Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
|
WB
Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
|
Next Generation Sequencing
Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
|
ICC/IF
Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
Images
-
2 bp deletion after Cys47 of the WT protein
-
All lanes : Anti-EpCAM antibody [E144] (ab32392) at 1/2000 dilution
Lane 1 : Wild-type A431 cell lysate
Lane 2 : EPCAM knockout A431 cell lysate
Lane 3 : MCF7 (Human breast adenocarcinoma cell line) whole cell lysate
Lane 4 : HeLa (Human epithelial cell line from cervix adenocarcinoma) whole cell lysate
Lysates/proteins at 20 µg per lane.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Observed band size: 40 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?Lanes 1 - 4: Merged signal (red and green). Green - ab32392 observed at 40 kDa. Red - loading control ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] observed at 55kDa.
ab32392 was shown to react with EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells in western blot with loss of signal observed in EpCAM knockout cell line ab261902 (knockout cell lysate ab263942). Wild-type and EpCAM knockout A-431 cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Membranes were blocked in fluorescent western blot (TBS-based) blocking solution before incubation with ab32392 and ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] overnight at 4°C at a 1 in 2000 dilution and a 1 in 20000 dilution respectively. Blots were incubated with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (IRDye® 800CW) preabsorbed (ab216773) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG H&L (IRDye® 680RD) preabsorbed (ab216776) secondary antibodies at 1 in 20000 dilution for 1 hour at room temperature before imaging.
-
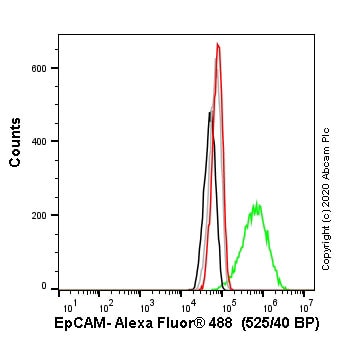
Flow cytometry overlay histogram showing wild-type A-431 (green line) and EPCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) stained with ab223582 (red line). The cells were incubated in 1x PBS containing 10% normal goat serum to block non-specific protein-protein interaction followed by the antibody (ab223582) (1x106 in 100μl at 0.2 μg/ml) for 30 min at 4°C.
The secondary antibody Goat anti-rabbit IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488, pre-adsorbed) (ab150081) was used at 1/2000 for 30 min at 4°C.
Isotype control antibody was Rabbit IgG (monoclonal) (ab172730) used at the same concentration and conditions as the primary antibody (wild-type A-431 - black line; EPCAM knockout A-431 - grey line). Unlabelled sample was also used as a control (this line is not shown for the purpose of simplicity).
Acquisition of >5000 events were collected using a 50 mW Blue laser (488nm) and 525/40 bandpass filter.
-
Knockout achieved by CRISPR/Cas9; X = 2 bp deletion; Frameshift: 99.58%
-
ab187372 staining EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells (top panel) and EpCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) (bottom panel). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (10 min) then permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 5 minutes and then blocked with 1% BSA/10% normal goat serum/0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h. The cells were then incubated with ab187372 at 0.1ug/ml concentration and ab6046 (Rabbit polyclonal to beta Tubulin) at 1/1000 dilution overnight at 4oC followed by a further incubation at room temperature for 1h with a goat secondary antibody to mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150117) at 2 ug/ml (shown in green) and a goat secondary antibody to rabbit IgG (Alexa Fluor® 594) (ab150080) at 2 ug/ml (shown in red). Nuclear DNA was labelled in blue with DAPI. This antibody performed similarly using 100% methanol fixation. Image was acquired with a high-content analyser (Operetta CLS, Perkin Elmer) and a single confocal section is shown.
-
All lanes : Anti-EpCAM antibody [EPR20532-222] (ab213500) at 1/1000 dilution
Lane 1 : Wild-type A431 whole cell lysate
Lane 2 : EPCAM knockout A431 whole cell lysate
Lane 3 : HeLa whole cell lysate
Lysates/proteins at 20 µg per lane.
Performed under reducing conditions.Lanes 1 - 3: Merged signal (red and green). Green - ab213500 observed at 40 kDa. Red - loading control, ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] observed at 55kDa.
ab213500 was shown to react with EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells in Western blot Loss of signal was observed when EpCAM knockout cell line ab261902 (knockout cell lysate ab263942) was used. Wild-type A-431 and EpCAM knockout cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Membranes were blocked in 3% milk in TBS-T (0.1% Tween®) before incubation with ab213500 and ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] overnight at 4°C at a 1 in 1000 dilution and a 1 in 20000 dilution respectively. Blots were developed with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (IRDye® 800CW) preabsorbed (ab216773) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG H&L (IRDye® 680RD) preabsorbed (ab216776) secondary antibodies at 1 in 20000 dilution for 1 hour at room temperature before imaging.
-
All lanes : Anti-EpCAM antibody [4A7] - C-terminal (ab224826) at 1/400 dilution
Lane 1 : Wild-type A-431 (Human epidermoid carcinoma cell line) whole cell lysate
Lane 2 : EPCAM knockout A-431 (Human epidermoid carcinoma cell line) whole cell lysate
Lane 3 : MCF7 (Human breast adenocarcinoma cell line) whole cell lysate
Lane 4 : HeLa (Human epithelial cell line from cervix adenocarcinoma) whole cell lysate
Lysates/proteins at 20 µg per lane.
Performed under reducing conditions.
Observed band size: 35 kDa why is the actual band size different from the predicted?Lanes 1 - 4: Merged signal (red and green). Green - ab224826 observed at 35 kDa. Red - loading control, ab52866 (Rabbit anti-alpha Tubulin antibody [EP1332Y]) observed at 55kDa.
ab224826 was shown to react with EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells in Western blot Loss of signal was observed when EpCAM knockout cell line ab261902 (knockout cell lysate ab263942) was used. Wild-type A-431 and EpCAM knockout cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Membranes were blocked in 3% milk in TBS-T (0.1% Tween®) before incubation with ab224826 and ab52866 (Rabbit anti-alpha Tubulin antibody [EP1332Y]) overnight at 4°C at a 1 in 400 dilution and a 1 in 20000 dilution respectively. Blots were developed with Goat anti-Mouse IgG H&L (IRDye® 800CW) preabsorbed (ab216772) and Goat anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (IRDye® 680RD) preabsorbed (ab216777) secondary antibodies at 1 in 20000 dilution for 1 hour at room temperature before imaging.
-
All lanes : Anti-EpCAM antibody [EPR20532-225] (ab223582) at 1/1000 dilution
Lane 1 : Wild-type A-431 (Human epidermoid carcinoma cell line) whole cell lysate
Lane 2 : EPCAM knockout A-431 (Human epidermoid carcinoma cell line) whole cell lysate
Lane 3 : HeLa (Human epithelial cell line from cervix adenocarcinoma) whole cell lysate
Lysates/proteins at 20 µg per lane.
Performed under reducing conditions.Lanes 1 - 3: Merged signal (red and green). Green - ab223582 observed at 40 kDa. Red - loading control, ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] observed at 55kDa.
ab223582 was shown to react with EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells in Western blot Loss of signal was observed when EpCAM knockout cell line ab261902 (knockout cell lysate ab263942) was used. Wild-type A-431 and EpCAM knockout cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Membranes were blocked in 3% milk in TBS-T (0.1% Tween®) before incubation with ab223582 and ab7291 (Mouse anti-Alpha Tubulin [DM1A] overnight at 4°C at a 1 in 1000 dilution and a 1 in 20000 dilution respectively. Blots were developed with Goat anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (IRDye® 800CW) preabsorbed (ab216773) and Goat anti-Mouse IgG H&L (IRDye® 680RD) preabsorbed (ab216776) secondary antibodies at 1 in 20000 dilution for 1 hour at room temperature before imaging.
-
ab85987 staining EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells (top panel) and EpCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) (bottom panel). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (10 min) then permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 5 minutes and then blocked with 1% BSA/10% normal goat serum/0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h. The cells were then incubated with ab85987 at 0.1ug/ml concentration and ab6046 (Rabbit polyclonal to beta Tubulin) at 1/1000 dilution overnight at 4oC followed by a further incubation at room temperature for 1h with a goat secondary antibody to mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150117) at 2 ug/ml (shown in green) and a goat secondary antibody to rabbit IgG (Alexa Fluor® 594) (ab150080) at 2 ug/ml (shown in red). Nuclear DNA was labelled in blue with DAPI. This antibody performed similarly using 100% methanol fixation. Image was acquired with a high-content analyser (Operetta CLS, Perkin Elmer) and a single confocal section is shown.
-
ab223582 staining EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells (top panel) and EpCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) (bottom panel). The cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (10 min) then permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 5 minutes and then blocked with 1% BSA/10% normal goat serum/0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h. The cells were then incubated with ab223582 at 0.1ug/ml concentration and ab7291 (Mouse monoclonal to alpha Tubulin) at 1/1000 dilution overnight at 4oC followed by a further incubation at room temperature for 1h with a goat secondary antibody to rabbit IgG (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150081) at 2 ug/ml (shown in green) and a goat secondary antibody to mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor® 594) (ab150120) at 2 ug/ml (shown in red). Nuclear DNA was labelled in blue with DAPI. This antibody performed similarly using 100% methanol fixation. Image was acquired with a high-content analyser (Operetta CLS, Perkin Elmer) and a single confocal section is shown.
-
ab187372 staining EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells (top panel) and EpCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) (bottom panel). The cells were fixed with 100% methanol (5 min) then permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 5 minutes and then blocked with 1% BSA/10% normal goat serum/0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h. The cells were then incubated with ab187372 at 0.5μg/ml concentration and ab6046 (Rabbit polyclonal to beta Tubulin) at 1/1000 dilution overnight at 4°C followed by a further incubation at room temperature for 1h with a goat secondary antibody to mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150117) at 2 μg/ml (shown in green) and a goat secondary antibody to rabbit IgG (Alexa Fluor® 594) (ab150080) at 2 μg/ml (shown in red). Nuclear DNA was labelled in blue with DAPI.
Image was taken with a confocal microscope (Leica-Microsystems TCS SP8). -
ab223582 staining EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells (top panel) and EpCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) (bottom panel). The cells were fixed with 100% methanol (5 min) then permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 5 minutes and then blocked with 1% BSA/10% normal goat serum/0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h. The cells were then incubated with ab223582 at 1/5000 dilution and ab7291 (Mouse monoclonal to alpha Tubulin) at 1/1000 dilution overnight at 4°C followed by a further incubation at room temperature for 1h with a goat secondary antibody to rabbit IgG (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150081) at 2 μg/ml (shown in green) and a goat secondary antibody to mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor® 594) (ab150120) at 2 μg/ml (shown in red). Nuclear DNA was labelled in blue with DAPI.
Image was taken with a confocal microscope (Leica-Microsystems TCS SP8). -
ab85987 staining EpCAM in wild-type A-431 cells (top panel) and EpCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) (bottom panel). The cells were fixed with 100% methanol (5 min) then permeabilized with 0.1% PBS-Tween for 5 minutes and then blocked with 1% BSA/10% normal goat serum/0.3M glycine in 0.1% PBS-Tween for 1h. The cells were then incubated with ab85987 at 0.5μg/ml concentration and ab6046 (Rabbit polyclonal to beta Tubulin) at 1/1000 dilution overnight at 4°C followed by a further incubation at room temperature for 1h with a goat secondary antibody to mouse IgG (Alexa Fluor® 488) (ab150117) at 2 μg/ml (shown in green) and a goat secondary antibody to rabbit IgG (Alexa Fluor® 594) (ab150080) at 2 μg/ml (shown in red). Nuclear DNA was labelled in blue with DAPI.
Image was taken with a confocal microscope (Leica-Microsystems TCS SP8). -
Flow cytometry overlay histogram showing wild-type A-431 (green line) and EPCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) stained with ab187372 (red line). The cells were incubated in 1x PBS containing 10% normal goat serum to block non-specific protein-protein interaction followed by the antibody (ab187372) (1x106 in 100μl at 0.2 μg/ml) for 30 min at 4°C.
The secondary antibody Goat anti-mouse IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488, pre-adsorbed) (ab150117) was used at 1/2000 for 30 min at 4°C.
Isotype control antibody was mouse IgG1κ (ab170190) used at the same concentration and conditions as the primary antibody (wild-type A-431 - black line; EPCAM knockout A-431 - grey line). Unlabelled sample was also used as a control (this line is not shown for the purpose of simplicity).
Acquisition of >5000 events were collected using a 50 mW Blue laser (488nm) and 525/40 bandpass filter.
-
Flow cytometry overlay histogram showing wild-type A-431 (green line) and EPCAM knockout A-431 cells (ab261902) stained with ab85987 (red line). The cells were incubated in 1x PBS containing 10% normal goat serum to block non-specific protein-protein interaction followed by the antibody (ab85987) (1x106 in 100μl at 0.2 μg/ml) for 30 min at 4°C.
The secondary antibody Goat anti-mouse IgG H&L (Alexa Fluor® 488, pre-adsorbed) (ab150117) was used at 1/2000 for 30 min at 4°C.
Isotype control antibody was mouse IgG1κ (ab170190) used at the same concentration and conditions as the primary antibody (wild-type A-431 - black line; EPCAM knockout A-431 - grey line). Unlabelled sample was also used as a control (this line is not shown for the purpose of simplicity).
Acquisition of >5000 events were collected using a 50 mW Blue laser (488nm) and 525/40 bandpass filter.
Protocols
Datasheets and documents
-
SDS download
-
Datasheet download
References (0)
ab261902 has not yet been referenced specifically in any publications.